In recent years, with the development of space research, the concept of light-year has emerged. While determining distances in space in light-years is easier and more understandable, the size of the universe has once again been revealed.
Contrary to popular belief, a light-year is a unit of distance, not a unit of time. One light-year is exactly 9,460,730,472,580.8 km (5.88 trillion miles).
When did the concept of light-year emerge? Why Did It Appear? Let’s examine together where the light-year is used.
Light-Year and Speed Of Light
The light-year unit was first introduced in 1838 by Friedrich Bessel after the first successful measurement of the distance to a star other than the Sun.
The speed of light was not yet precisely known in 1838; the estimate of its value changed in 1849 (Fizeau) and 1862 (Foucault). It was not yet considered to be a fundamental constant of nature, and the propagation of light through the aether or space was still enigmatic.
The light-year unit appeared in 1851 in a German popular astronomical article by Otto Ule. Ule explained the oddity of a distance unit name ending in “year” by comparing it to a walking hour (Wegstunde).
The speed of light in vacuum, commonly denoted c, is a universal physical constant that is exactly equal to 299,792,458 metres per second (approximately 300,000 kilometres per second; 186,000 miles per second; 671 million miles per hour).
If you travel at the speed of light for 1 year, you will travel one light-year.
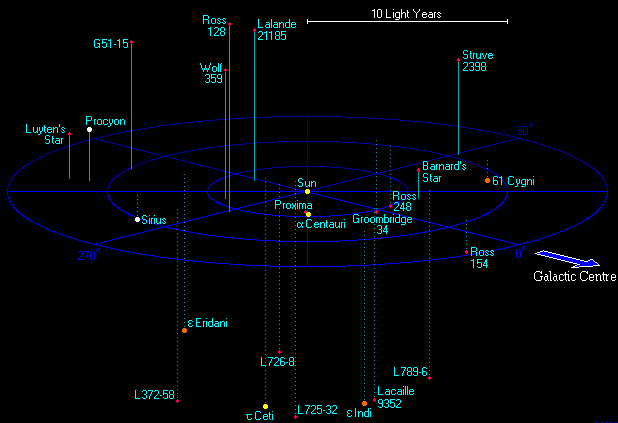
Distances expressed in light-years include those between stars in the same general area, such as those belonging to the same spiral arm or globular cluster. Galaxies themselves span from a few thousand to a few hundred thousand light-years in diameter, and are separated from neighbouring galaxies and galaxy clusters by millions of light-years. Distances to objects such as quasars and the Sloan Great Wall run up into the billions of light-years.
Approximate speed of light travel times
If you move at the speed of light, you can check the time it takes to reach certain distances in the table below.
| Distance | Time |
|---|---|
| one foot | 1.0 ns |
| one metre | 3.3 ns |
| from geostationary orbit to Earth | 119 ms |
| the length of Earth’s equator | 134 ms |
| from Moon to Earth | 1.3 s |
| from Sun to Earth (1 AU) | 8.3 min |
| one light-year | 1.0 year |
| one parsec | 3.26 years |
| from the nearest star to Sun (1.3 pc) | 4.2 years |
| from the nearest galaxy to Earth | 70000 years |
| across the Milky Way | 87400 years |
| from the Andromeda Galaxy to Earth | 2.5 million years |
Although modern astronomers often prefer to use the parsec, light-years are also popularly used to gauge the expanses of interstellar and intergalactic space.

A beam of light is depicted travelling between the Earth and the Moon in the time it takes a light pulse to move between them: 1.255 seconds at their mean orbital (surface-to-surface) distance. The relative sizes and separation of the Earth–Moon system are shown to scale.
Can We Travel Faster Than Light?
As we explained, the speed of light is a speed we cannot reach with our current technology. “Warp speed” is featured in science fiction movies and theories. The idea of traveling faster than light is the subject of science fiction movies. With warp speed, that is, faster-than-light travel, very long distances can be crossed in space in a very short time.
But it is a fact that faster than light travel is currently impossible. For warp speed to happen, we will need to leverage and transcend physics, engineering, and science. Fortunately, there are many avenues to explore for science fiction enthusiasts and theoretical physicists alike.
Source: Wikipedia




